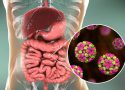
Norovirus is a highly contagious virus and the most common viral foodborne illness. Norovirus infection is acquired by consuming produce (fruit and vegetables) irrigated with contaminated water contaminated with human or animal feces – or shellfish farmed or harvested in water contaminated with human sewage.
Because only a few norovirus particles can make people sick, infection can also occur by consuming food handled by a person infected with the virus – or being in direct contact with an object, surface, or person that has been infected.
Read More »